The South American plant from the family of Compositae hebruulia shoot (Chevreulia stolonifera) belongs to flight distance record. With air currents they are able to overcome a distance of more than 7.5 thousand. km
 He less than 12 thousand kilometers floated seeds of a typical creeper from the legume family - giant entada (Entada scandens). Large, up to 1 m long, beans of this plant able to spend more than a year in salt sea waterwithout losing seed germination.
He less than 12 thousand kilometers floated seeds of a typical creeper from the legume family - giant entada (Entada scandens). Large, up to 1 m long, beans of this plant able to spend more than a year in salt sea waterwithout losing seed germination.
About a year they can swim in fresh water, air-filled leather pouches around.
The most common weed, which has spread over more than 100 countries, is a permanent sedge - full round (Cyperus rotundus). Fortunately, in Russia, besides the Caucasus, it practically does not occur.
The Brazilian plant, water hyacinth, or Eichhornia thorny-footed (Eichhornia crassipes, from the nameless family Pontederiaceae) has spread almost in all large reservoirs, as well as in rivers and lakes in the tropical region of New Town and New malicious waterman.
One of the most salt tolerant mantle plants is soleroc (Salicornia europea, from the cough family). It grows on coasts and salt marshes with salt concentration in groundwater up to 6%. Ego seeds germinate even in a 10% salt solution.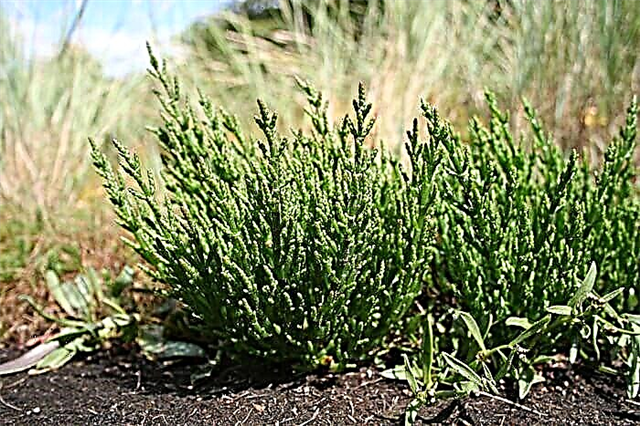
The second largest family of class monocotyledons is cereals; from 8 to 10 thousand species belong to it. Cereals are distributed throughout, they are found even on the extreme borders of vegetation distribution - in Antarctica and on the islands of the islands.
The green alga Dunaliella solonchakova (Dunaliella salina) can exist in saline oceax with a salt concentration of 285 g / l.
In the dicotyledon class, the largest family - complex colors. It includes about 900 genera, including from 13 to 20 thousand. Like cereals, complex ones are widespread everywhere - from the Arctic to the Antarctic, from plains to high mountains.
The northernmost point on Earth where a flowering plant is found - Alpine glade (Cerastium alpinum, from the family of carnations) - Lockwood Island, which is located in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago - 83-24 ns Further to the north, only some mosses and lichens are encountered. 
The southernmost border of the propagation of flowering plants runs between 64o and 66o s.sh. on the Antarctic continent and the Antarctic islands. Here, in the wetland – lichen deserts of Antarctica, two species of flowering plants are found - colobanthus platifolia (Colobanthus crassifolius, from the cloves family) and cereal pike anthracis trica des Antarctica. 
The highest growth rate has One of the relatives of bamboo is the edible leafworm (Phyllostachys edulis), found wild in the south of China. The daily increase in the run of this plant reaches 40 cm, i.e. 1.7 cm per hour. In just a few months, the leafwort grows to a 30-meter height, reaching 50 cm in diameter.
There are plants common on all continents of the Earth. They received the name Cosmopolitan. Five of the most widespread species include: shepherd's bag (Capsella bursa-pastoris, from the cruciferous family), cattle, or mountaineer bird (Polygonum aviculare), from the buckwheat family), annual bluegrass (Poa annua from cereals), starfish (starfish) Stellaria media, from the clove family) and dioica nettle (Urtica dioica, nettle family). 
The most diverse in number of species among flowering plants, hawk is considered (Hieracium, a family of Asteraceae). The species of species are very variable, in addition, there are many transitional forms. Therefore, the sizes of this water by different botanists are estimated from 1 to 5 thousand. species. 
Sedges are also a very large genus (Carex, family of sedge). Currently, according to estimates of sedge species, there are from 1.5 to 2 thousand species.
The oldest tree in the world It is also considered a bald plant - spinous coconut (Pinus longaeva or P. aristata), which grows in the mountains of Eastern Nevada. The radiocarbon analysis method showed that the size of this tree is about 4900 years.
Growing on sphagnum bogs of bilberry (Vaccinum myrtyllus) and cranberries (Oxycoccus palustris) from the lingonberry family (according to other views, from the heather family) able to tolerate very high soil acidity - pH is about 3.5.
In a wide range of soil acidity, some cultivated plants can grow. So, rye and sorghum are most indifferent to soil acidity and survive in the pH range from 4.5 to 8.0. Cereal and carrots do not tolerate very acidic soils, but quietly tolerate pH fluctuations from 5.0 to 8.5. 
One of the most “thick” trees African baobab (Adansonia digitata, from the bombing family) is counted in the world. The diameter of the trunk of the largest of the described baobabs was about 9 m. However, the diameter of a common edible European chestnut (Castanea sativa, a chestnut family), growing on Mount Etna in Sicily, in 1845 had a trunk about 20 m long 4 m in diameter. The age of this giant was estimated at 3600-4000 years. Giant aquatic cypresses (Taxodium mucronatum) are growing in Mexico - gymnosperms from the order of cypress, with a trunk diameter of 10.9 to 16.5 m.
The longest tree on the Earth is the liana-shaped palm rattan (genus Calamus, palm family). Its total length, according to various sources, reaches from 150 to 300 m. It is interesting that the diameter of the stem in the base at this does not exceed a few centimeters at the pitch. Rattan stalks stretch from a tree to a tree, holding on to supporting plants with strong spikes located on medium veins of large cirrus leaves.
The total length of all roots of the four winter rye plant is more than 619 km.
The largest leaves in the world Palma rafia tediger growing in Brazil (Raphia taedigera). With a 4–5-meter petiole, its clear leaf blade reaches a length of more than 20 m and a width of about 12 m. 
Largest single plate castings there is an Amazonian water lily - Victoria Amazonian (Victoria amazonica, synonym - V.regia, from the family of water lilies). Their diameter reaches 2 m, and the maximum "load capacity" with a uniform load - 80 kg. 
One of most large leaf buds (shortened future escapes) - a cabbage head. The weight of the cabbage head can reach more than 43 kg. 
The smallest flowering plant on Earth - Wolffia rootless (Wolffia arrhiza, from the Russian family) found in fresh waters of Australia and the tropics of the Old World. The tiny leaf of wolfia has a diameter of 0.5–2 mm. In this case, the plant is able to form rather large clusters, tightening the surface of the water reservoirs with a continuous film, similar to ordinary duckweed. 
Wolffia Beskornova and her cousins are Lemna minor and the smallest flowers. Their diameter does not exceed 0.5 mm. 
The largest inflorescences the palm of Corifa umbelliferous (Corypha umbraculifera), which grows in south-east Asia and in Sri Lanka. The height of its inflorescence reaches 6 m, and the number of flowers in the inflorescence is half a million. 
Flowering Duration set a palm cariot burning, or kitul (Caryota urens). This tree, growing in south-western Asia, blooms once in a lifetime, after which it dies. However, flowering lasts continuously for several years. 
At an altitude of 6218 m above the sea level, a squat plant of a bryophyte (Arenaria musciformis, from the family of carnivores) rises into the mountains. A little lower, at an altitude of 6096 m, in the Himalayas, several species of edelweiss (Leontopodium) from the family Asteraceae grow.
Cultivated plants rise high into the mountains. In Central Asia, the land border reaches 5 thousand meters above sea level. In Tibet, barley is grown at this height.
The largest fruits in the world grow on a herbaceous plant of an ordinary pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo) - they can have a weight of more than 92 kg.
The smallest among flowering plants seeds has a parasitic zarazixa plant (Orobanche ionantha, from the broomrape family). Bec of one seed is only one hundredth of a gram. 
About 45 species of flower plants are so original that separate families were established for them - with a single genus and one species. Most of these plants are inhabitants of the tropical and subtropics. And in the temperate zone there are muscular adoxa (Adoxa moschatellina) and umbrella gum (Butomus umbellatus) - the only representatives of the families, respectively, of adolescents and susaks.
The largest tubers (modified underground shoots) forms the plant Asian Yams (Dioscorea alata, from the dioscoreic family). Tubers of cultivated yam can reach a mass of 50 kg. They are eaten baked or vape, and taste like potatoes. 
The leaves of Stevia Pebo (Stevia rebaudiana) - plants from the family Asteraceae, a native of South America - contain glycosides Stevin and rebodin, which 300 times sweeter than sugar.
Most protein in seeds - 61% - contains legumes of lupine (genus Lupinus). However, along with protein, lupine seeds contain toxic alkaloids, which does not allow their use in food. 
The Cuban tree exogenous bristle (Aeschynomene hispida, from the family of legumes) has the lightest wood in the world. Its density is only 0.044 g / cm3, which is 23 times less than the density of water and 3 times lighter than the tree of the famous balsa tree. The Kon-Tiki raft, on which the famous traveler Tur Heyerdahl crosses the Pacific Ocean, was made from the wood of a white tree.
The largest flower in the world - in a tropical plant of tropical forests of the west of Sumatra, described in 1821 - the affliction of Arnold (Rafflesia arnoldi, from the family of afflicted). Currently, its maximum dimensions are estimated at 45 cm in diameter with a mass of 7 kg. 
Record holder for the area occupied by the crown, Indian banyan, or Ficus bengalis (Ficus bengalensis, from the family of mulberries,) is considered. This ficus forms a large number of aerial roots on the lateral branches, which, reaching the ground, are shortened and turn into false trunks. As a result, the huge crown of the tree is held on root props. The most famous of the banyan trees grows in the botanical garden of the city of Calcutta. In 1929, when measurements were taken, the circumference of its crown exceeded 300 m (slightly less than 100 m across), and the number of “trunks” - air roots - reached 600. 
Nelumbo nucifera, a lotus seed family, discovered in 1951 in Japan, in a peat bog at a depth of 5.5 m, was located in a boat belonging to a man of the Stone Age. After extracting them from the peat, they sprouted, the streams normally developed and bloomed. The burial of these seeds in peat without the availability of oxygen contributed to the preservation of their viability. The radiocarbon analysis method showed that by Seeds were at least 1040 years old. 
The largest companies characteristic of a breadfruit tree from the mulberry family, more precisely - one of its species, jackfruit (Arctocarpus heterophyllus). The weight of one fertility is about 40 kg, length - about 90 cm, width - up to 50 cm.
The largest pollen grains - their diameter is 250 microns - have ordinary pumpkin. AND the smallest pollen formed in the anthers of forget-me-nots (Myosotis sylvatica) - 2–5 microns. It is interesting that both plants are insect pollinated. In windy plants, the diameter of pollen grains is, on average, 20–50 microns. 
The highest tree on Earth is currently considered to be the evergreen (Sequoia sempervirens) Hyperion. The largest of the trees reliably measured in the last century in the National Park of the USA, had a height of 120 m and was called the “Father of Forests”. Sequoia is evergreen and sequoia dendron, or mammoth tree (Sequoiadendron giganteum) is close in size. However, these plants belong to gymnosperms (the order of cypress), and the highest flowering plants on the Earth are Australian eucalyptus trees (Eucalyptus, a family of dead). The highest eucalyptus treesexisting now, two trees are considered, related to the species of eucalyptus flower (Eucalyptus regnans). One of them has a height of 99.4 m, and the other - 98.1 m. 
The most “heat-resistant” land plant is a camel thorn (Alhagi camelorum, from the legume family). It can withstand temperatures up to +70 oC. 
The shoots of the trees of the genera birch (Betula, family of birch), poplar (Populus, family of willow) and - from starved - larch (Larix) very cold resistant. They are able to withstand cooling to –196 ° C. Blackcurrant cuttings (Ribes nigrum, from the gooseberry family) are able to withstand cooling to –253 ° C without losing any rooting ability after thawing. However, this is a potential cold resistance of plants, established in laboratory conditions. At the pole of the cold in the northern hemisphere of birch and larch, the temperature drops to –71 ° C. 
And finally, there are some more interesting facts related to other groups of plants and mushrooms.
The largest water supply - brown water macrocystis (Macrocystis pyrifera). Its maximum length, according to various sources, ranges from 70 to 300 m. 
Water immersion rating is also the brown alga of the laminaria Rodpigeca (Laminaria rodriguesii). In the Adriatic Sea, it was raised from a depth of about 200 m. 
And here is a blue-green algae filamentous oscilloscope (Oscillatoria filiformis) perfectly lives and breeds in hot spring water, the temperature in which reaches +85.2 ° C. 
Cladonia bushy lichens in the dried state remain alive after heating to +101 ° C. And moss barbul slender (Barbula gracilis) retains viability even after keeping it at a temperature of + 110-115 ° C for 30 minutes.
The title of the most drought-tolerant plant claims sea brown algae - bubbly fucus (Fucus vesiculosus). It tolerates moisture loss ten times the original content. By the way, this and the most frost-resistant among algae. Fucus withstands temperatures up to –60 ° C. 
The growth rate of the fruiting body of the fungus the vera ordinary (Phallus impudicus) is twice the rate of growth of the shoots of the leaves, reaching 5 mm per minute. 
The most dense wood, which is 1.5 times heavier than water, has a piratinera (genus Piratinera, from the tutaceae family), growing in Guyana. Almost the same dense wood has a guayakoe, or a bacouta tree (Guajacium officinale, from the family of leaf leaves). Its density is 1.42 g / cm3. As a rule, the wood of the bacouta tree almost does not lose iron.